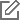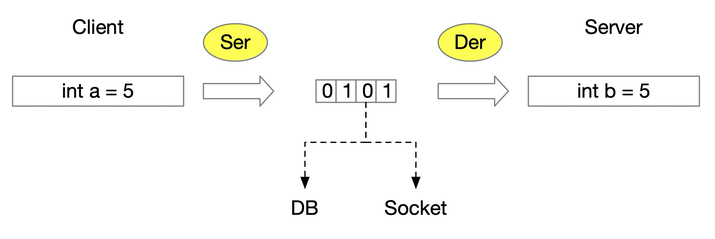
序列化协议 |
特点 |
jdk |
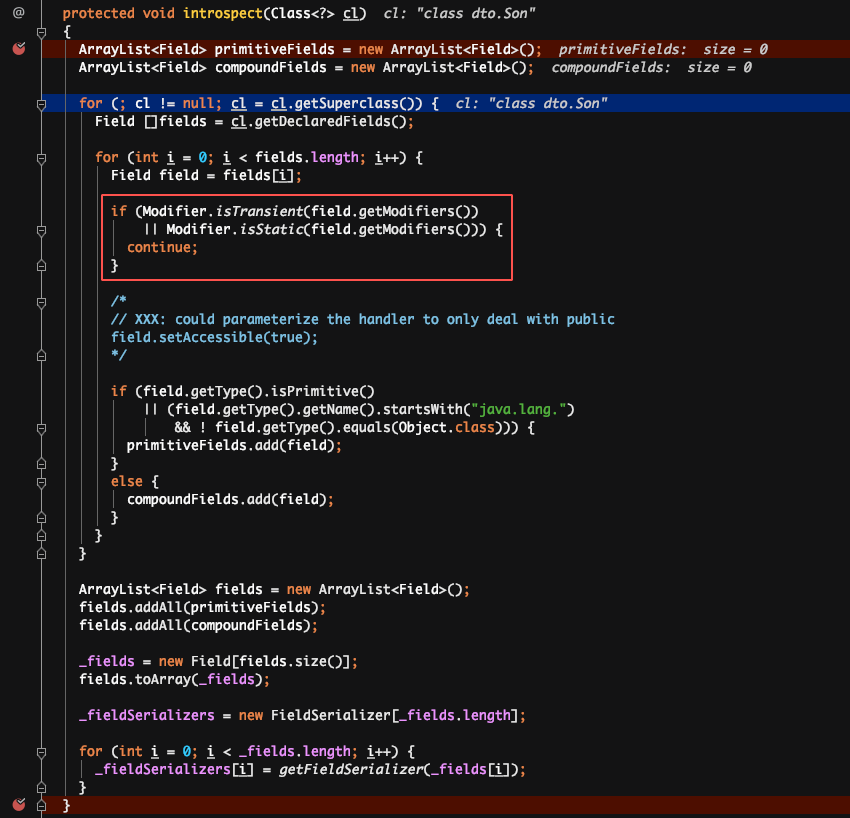
1. 序列化:除了 static、transient类型 |
fastjson |
1. 可读性好,空间占用小 |
hessian |
1. 序列化:除了 static、transient 类型 |
Father father = new Father();
father.name = "厨师";
father.comment = "川菜馆";
father.simpleInt = 1;
father.boxInt = new Integer(10);
father.simpleDouble = 1;
father.boxDouble = new Double(10);
father.bigDecimal = new BigDecimal(11.5);
jdk序列化结果长度:626,耗时:55
jdk反序列化结果:Father{version=0, name='厨师', comment='川菜馆', boxInt=10, simpleInt=1, boxDouble=10.0, simpleDouble=1.0, bigDecimal=11.5}耗时:87
hessian序列化结果长度:182,耗时:56
hessian反序列化结果:Father{version=0, name='厨师', comment='川菜馆', boxInt=10, simpleInt=1, boxDouble=10.0, simpleDouble=1.0, bigDecimal=11.5}耗时:7
Fastjson序列化结果长度:119,耗时:225
Fastjson反序列化结果:Father{version=0, name='厨师', comment='川菜馆', boxInt=10, simpleInt=1, boxDouble=10.0, simpleDouble=1.0, bigDecimal=11.5}耗时:69
public class Father implements Serializable {
/**
* 静态类型不会被序列化
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* transient 不会被序列化
*/
transient int version = 0;
/**
* 名称
*/
public String name;
/**
* 备注
*/
public String comment;
/**
* 包装器类型1
*/
public Integer boxInt;
/**
* 基本类型1
*/
public int simpleInt;
/**
* 包装器类型2
*/
public Double boxDouble;
/**
* 基本类型2
*/
public double simpleDouble;
/**
* BigDecimal
*/
public BigDecimal bigDecimal;
public Father() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Father{" +
"version=" + version +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", comment='" + comment + '\'' +
", boxInt=" + boxInt +
", simpleInt=" + simpleInt +
", boxDouble=" + boxDouble +
", simpleDouble=" + simpleDouble +
", bigDecimal=" + bigDecimal +
'}';
}
}public class Son extends Father {
/**
* 名称,与father同名属性
*/
public String name;
/**
* 自定义类
*/
public Attributes attributes;
/**
* 枚举
*/
public Color color;
public Son() {
}
}public class Attributes implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public int value;
public String msg;
public Attributes() {
}
public Attributes(int value, String msg) {
this.value = value;
this.msg = msg;
}
}public enum Color {
RED(1, "red"),
YELLOW(2, "yellow")
;
public int value;
public String msg;
Color() {
}
Color(int value, String msg) {
this.value = value;
this.msg = msg;
}
}使用到的对象及属性设置
Son son = new Son();
son.name = "厨师"; // 父子类同名字段,只给子类属性赋值
son.comment = "川菜馆";
son.simpleInt = 1;
son.boxInt = new Integer(10);
son.simpleDouble = 1;
son.boxDouble = new Double(10);
son.bigDecimal = new BigDecimal(11.5);
son.color = Color.RED;
son.attributes = new Attributes(11, "hello");
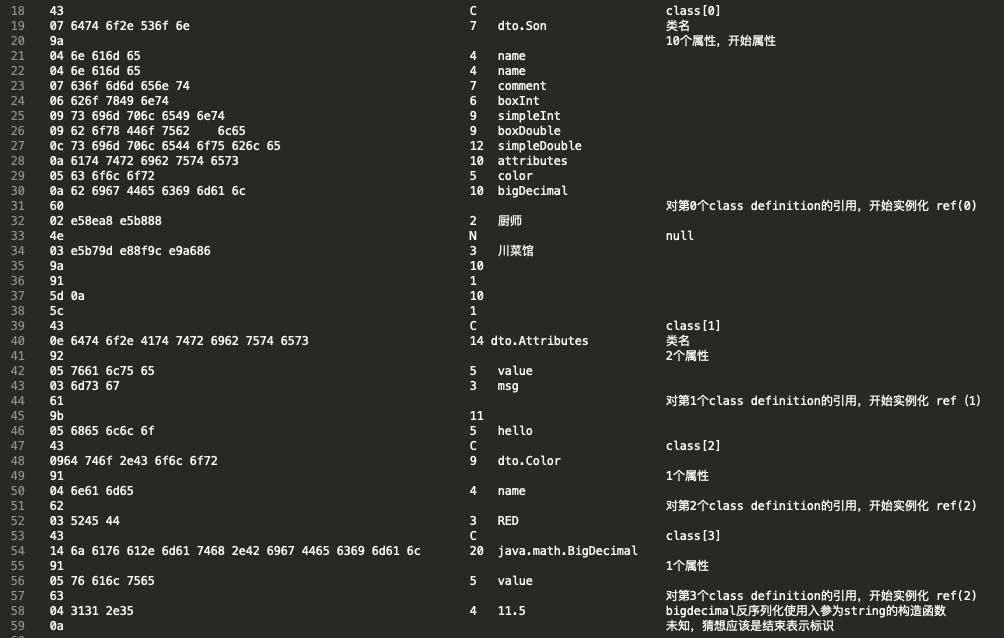
使用 Hessian 序列化,结果写入文件,使用 vim 打开。使用 16 进制方式查看,查看命令:%!xxd
00000000: 4307 6474 6f2e 536f 6e9a 046e 616d 6504 C.dto.Son..name.
00000010: 6e61 6d65 0763 6f6d 6d65 6e74 0662 6f78 name.comment.box
00000020: 496e 7409 7369 6d70 6c65 496e 7409 626f Int.simpleInt.bo
00000030: 7844 6f75 626c 650c 7369 6d70 6c65 446f xDouble.simpleDo
00000040: 7562 6c65 0a61 7474 7269 6275 7465 7305 uble.attributes.
00000050: 636f 6c6f 720a 6269 6744 6563 696d 616c color.bigDecimal
00000060: 6002 e58e a8e5 b888 4e03 e5b7 9de8 8f9c `.......N.......
00000070: e9a6 869a 915d 0a5c 430e 6474 6f2e 4174 .....].\C.dto.At
00000080: 7472 6962 7574 6573 9205 7661 6c75 6503 tributes..value.
00000090: 6d73 6761 9b05 6865 6c6c 6f43 0964 746f msga..helloC.dto
000000a0: 2e43 6f6c 6f72 9104 6e61 6d65 6203 5245 .Color..nameb.RE
000000b0: 4443 146a 6176 612e 6d61 7468 2e42 6967 DC.java.math.Big
000000c0: 4465 6369 6d61 6c91 0576 616c 7565 6304 Decimal..valuec.
000000d0: 3131 2e35 0a 11.5.
对其中的十六进制数逐个分析,可以拆解为一下结构:参考 hessian 官方文档,链接:http://hessian.caucho.com/doc/hessian-serialization.html
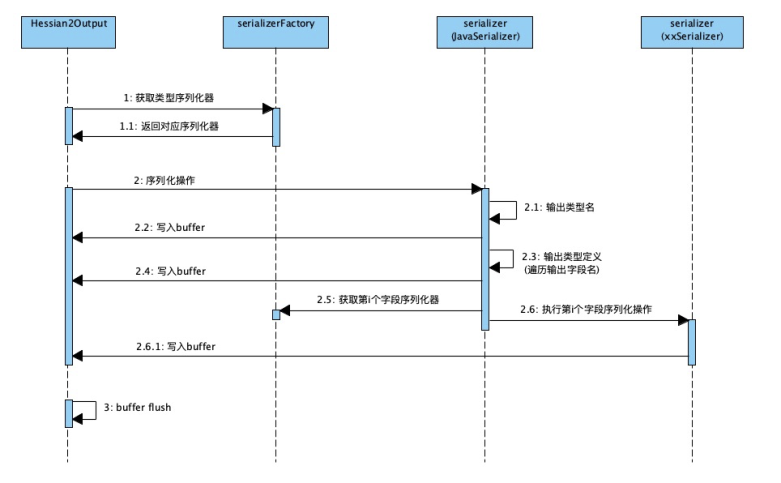

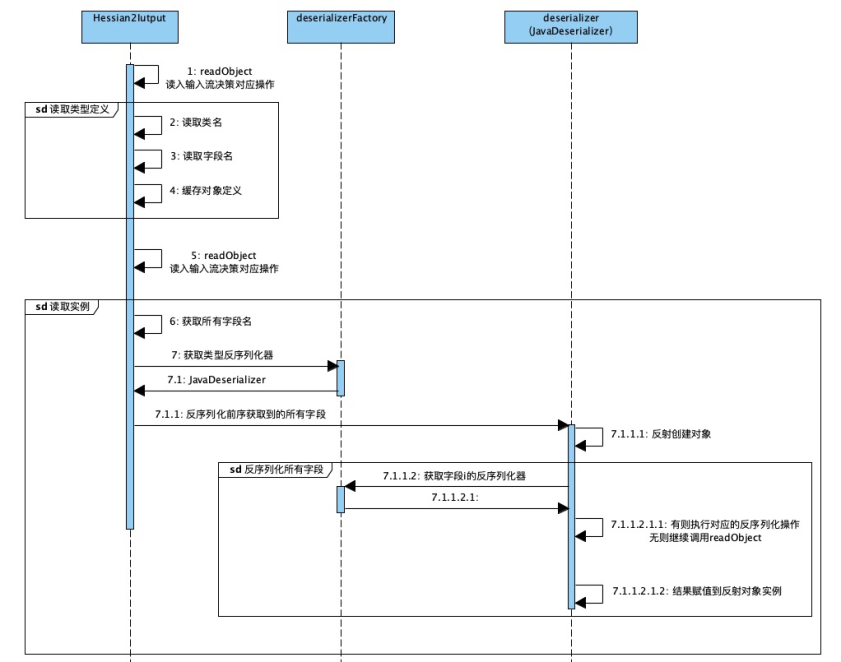
通俗原理图:
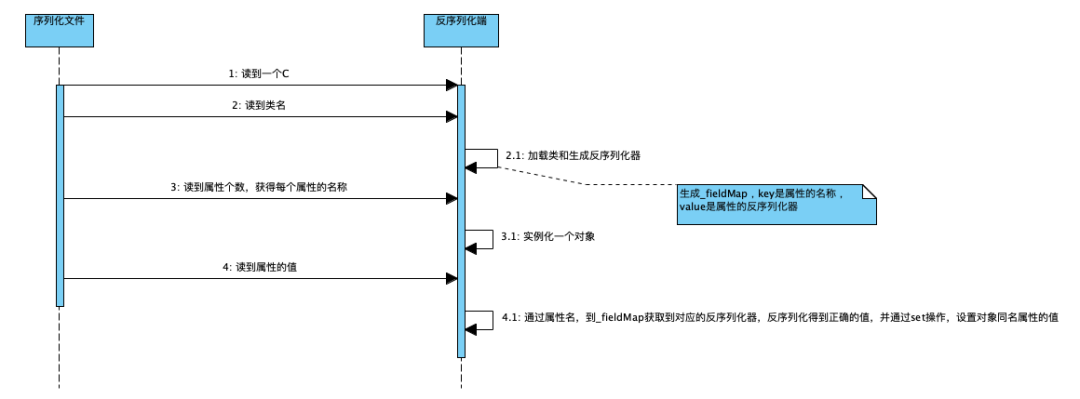
解释:这是前边的序列化文件,可以对着这个结构理解反序列化的过程。
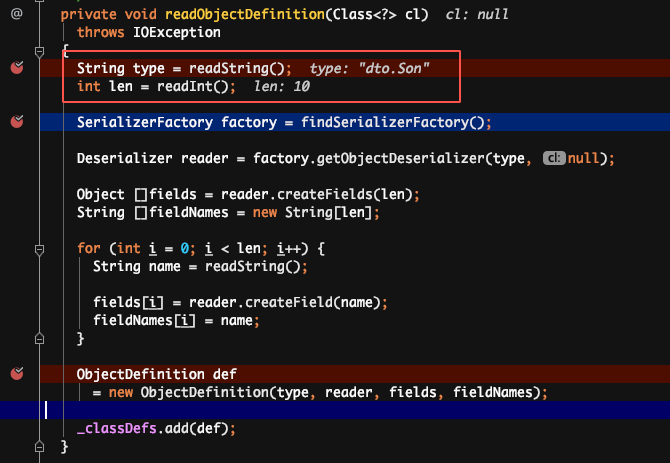
解释:读取到“C”之后,它就知道接下来是一个类的定义,接着就开始读取类名,属性个数和每个属性的名称。并把这个类的定义缓存到一个_classDefs 的 list 里。
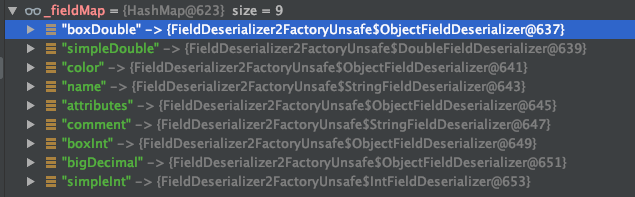
解释:通过读取序列化文件,获得类名后,会加载这个类,并生成这个类的反序列化器。这里会生成一个_fieldMap,key 为反序列化端这个类所有属性的名称,value 为属性对应的反序列化器。
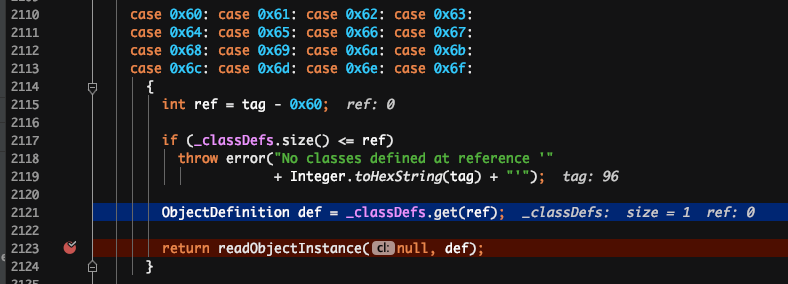
解释:读到 6 打头的 2 位十六进制数时,开始类的实例化和赋值。

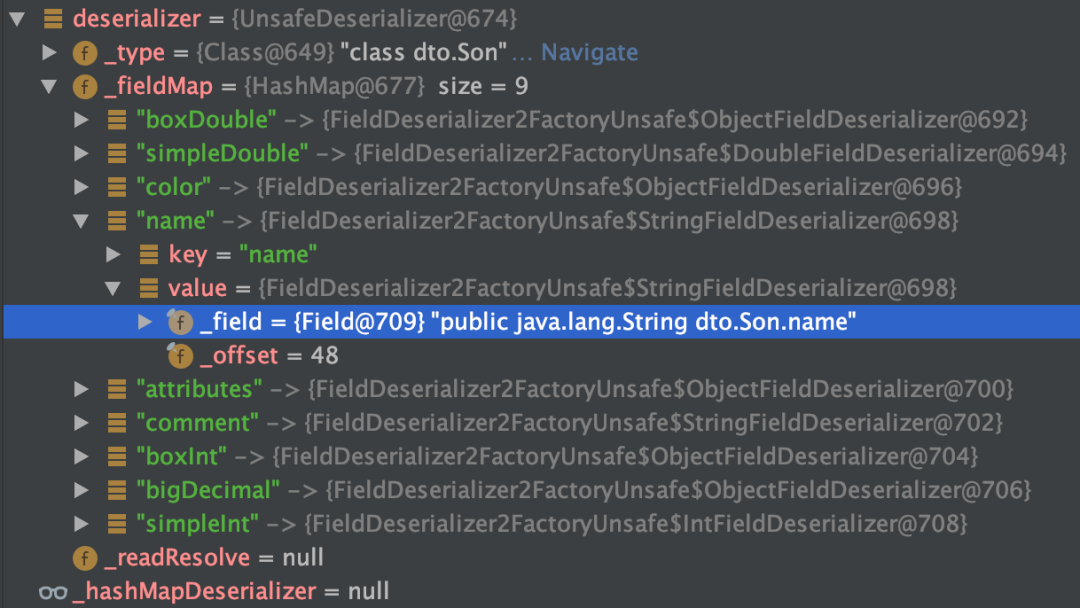


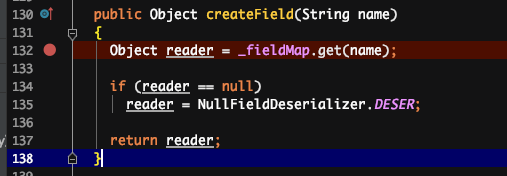
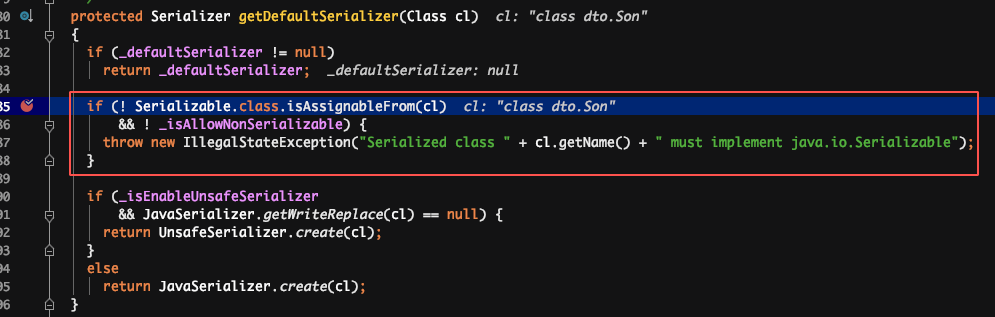
原因:反序列化时,是先通过类名加载同名类,并生成同名类的反序列化器,同名类每个属性对应的反序列化器存储在一个 map 中。在反序列化二进制文件时,通过读取到的属性名,到 map 中获取对应的反序列化器。若获取不到,默认是 NullFieldDeserializer.DESER。待到读值的时候,仅读值,不作 set 操作


 暂无任何评论,欢迎留下你的想法
暂无任何评论,欢迎留下你的想法